Industrial steam boilers are essential devices used across various industries to generate steam, which is then utilized for multiple processes such as power generation, heating, and sterilization. These boilers operate by applying heat to water, converting it into steam, which is then distributed for industrial use. To fully understand how industrial steam boilers work, we can break down the process into several key stages:
1. Heat Source

The operation of an industrial steam boiler begins with a heat source. Typically, this involves the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, oil, coal, or biomass. In gas-fired boilers, like those offered by Tuff Boilers, low-NOx emissions technology is used to ensure cleaner combustion and reduced environmental impact. For some applications, electric boilers are used, where electricity provides the heat instead of combustion. The fuel is burned inside the combustion chamber, producing heat that is transferred to the water in the boiler.
2. Water Supply

For the boiler to generate steam, it requires a continuous supply of water. This is managed by the feedwater system, which ensures that the boiler always has enough water to operate efficiently. The water is often treated to remove impurities like minerals and chemicals, which helps to prevent corrosion and scaling inside the boiler. Treated water extends the lifespan of the boiler and ensures optimal performance. The water is stored in the pressure vessel, which is designed to hold water and steam under high pressure.
3. Heat Transfer
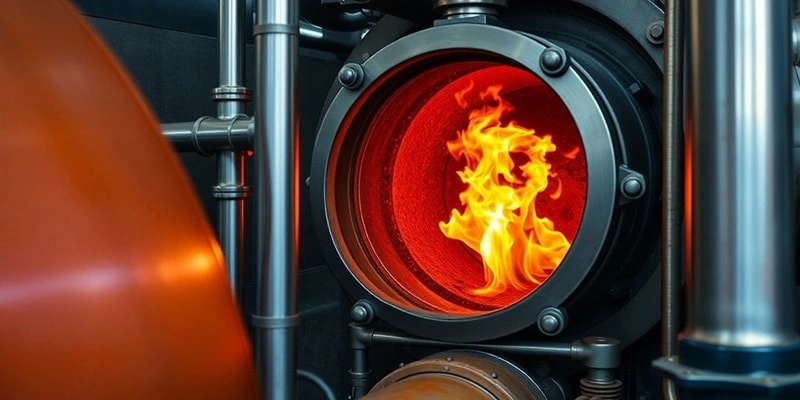

Once the fuel is burned, the heat generated must be transferred to the water. This process of heat transfer varies depending on the boiler type:
Fire-tube boilers: In this design, hot combustion gases pass through tubes that are surrounded by water. The heat from the gases passes through the tube walls, heating the surrounding water and converting it into steam. Fire-tube boilers are often used for low to medium pressure applications.
Water-tube boilers: In this design, water circulates through tubes that are heated externally by the combustion gases. The heat causes the water inside the tubes to turn into steam. This configuration is more common for high-pressure applications such as power generation because of the boiler’s ability to handle greater pressures and temperatures.
Tuff Boilers offers both fire-tube and water-tube designs, ensuring that each customer can find the right boiler for their specific operational needs.
4. Steam Generation
As the water continues to absorb heat, it reaches its boiling point and starts to convert into steam. In most industrial boilers, the steam is generated at high pressures and high temperatures, which allows it to carry more energy. The steam rises to the top of the boiler, where it is collected in a steam drum or space within the pressure vessel. At this point, the steam is ready for distribution.
5. Steam Distribution
Once the steam has been produced, it is directed into a steam distribution system, which delivers it to the equipment or processes that require it. Steam can be used for a variety of industrial applications, including:
Heating: Steam is used to heat large spaces in industrial facilities or to heat fluids involved in specific manufacturing processes.
Power Generation: In power plants, steam drives turbines that generate electricity.
Sterilization and Cleaning: Steam is a common method for sterilizing equipment in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare.
With Tuff Boilers’ advanced control systems, the precise delivery of steam to these applications is managed efficiently, ensuring that energy is used effectively and that downtime is minimized.
6. Condensation and Return
After the steam has served its purpose in the industrial process, it cools down and condenses back into water. This condensate is collected and often returned to the boiler through a condensate return system. Reusing the condensate improves the overall energy efficiency of the system, as the water is already hot and requires less energy to be reheated. This is a crucial step in maintaining the boiler’s efficiency and reducing operational costs.
7.Control Systems
Modern industrial boilers are equipped with sophisticated control systems that monitor and regulate various operating parameters, such as pressure, temperature, and water levels. These systems ensure that the boiler operates within safe limits and at maximum efficiency. Tuff Boilers integrates IoT-based monitoring systems, allowing operators to supervise boiler performance in real time, adjust settings remotely, and receive alerts for any operational issues. This advanced technology significantly enhances safety, uptime, and energy savings.
Summary of Key Components
|
Component |
Function |
|
Combustion Chamber |
Burns fuel to generate heat for steam production |
|
Feedwater System |
Ensures a continuous supply of water to the boiler |
|
Pressure Vessel |
Contains water and steam under high pressure |
|
Heat Exchanger |
Transfers heat from combustion gases to the water |
|
Steam Distribution |
Delivers steam to the equipment or processes that require it |
|
Control System |
Monitors and regulates temperature, pressure, and water levels for efficiency |
Why Choose TUFF Boilers?
The entire process of an industrial steam boiler is a continuous cycle of combustion, heating, and distribution, designed to maximize efficiency and meet the demands of industrial production.
Fuel and Combustion Process in Industrial Boilers
Types of Fuels Used
Industrial steam boilers rely on various fuels to generate heat. The choice of fuel can significantly affect the boiler’s efficiency and emissions. Here are some common fuels used:
Natural Gas: This is a popular choice due to its clean-burning properties and high efficiency.
Oil: While less common than natural gas, oil is still used, especially in areas lacking gas infrastructure.
Coal: Known for its high energy content, coal remains a significant source of heat, despite environmental concerns.
Biomass: This renewable option is gaining popularity, as it utilizes organic materials for combustion.
How Combustion Is Achieved Efficiently
Efficient combustion is crucial for maximizing heat output and minimizing emissions. To achieve this, the fuel must be mixed with air in the right proportions. Here are key factors that contribute to efficient combustion:
1.Fuel-to-Air Ratio: Maintaining the correct ratio ensures complete burning of the fuel.
2.Air Temperature and Velocity: Introducing air at the right temperature and speed helps create optimal flame conditions.
3.Burner Design: Industrial burners are designed to adapt to different fuels, ensuring effective combustion.
Role of Industrial Burners
Industrial burners play a vital role in the combustion process. They control how fuel and air enter the boiler, adjusting to meet demand. This adaptability helps maintain stable operation under varying conditions. Burners are engineered to match the specific characteristics of the fuel being used, which optimizes the combustion process and reduces waste.
In summary, the fuel and combustion process in industrial boilers is essential for efficient operation and environmental responsibility. Understanding the types of fuels, combustion efficiency, and the role of burners can help industries improve their energy use and reduce emissions.
Conclusion
Tuff Boilers stands at the forefront of boiler technology, offering highly efficient, low-emission steam boilers that incorporate cutting-edge features like IoT integration and remote monitoring. With decades of experience and a global presence, Tuff is trusted by industries worldwide to deliver reliable, sustainable, and high-performance boiler solutions. Whether you need a gas-fired boiler, an electric boiler, or a biomass boiler, Tuff has the expertise and technological innovation to meet your requirements.
Conclusion
In summary, industrial steam boilers use a heat source to convert water into steam, which is then distributed for various industrial applications. The process involves burning fuel (or using electricity), heating water, generating steam, and distributing it efficiently. Boilers are designed to operate at high efficiency while ensuring safety, and modern systems are equipped with advanced controls to minimize energy usage and maximize operational uptime. Tuff Boilers offers a wide range of customizable, high-efficiency steam boilers tailored to meet the unique needs of industries worldwide.